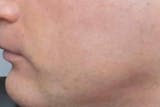
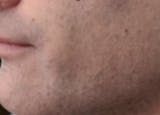
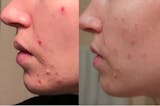
Oral steroids are a treatment option for eczema flares, reducing inflammation and providing relief during acute flares.
Oral steroids are not a long-term cure for eczema and flares can return after their use is ended if other strategies are not adopted.
Eczema is a chronic skin condition characterized by periodic acute flares, marked by red, itchy, and inflamed skin. The severity and duration of an acute eczema flare are influenced by three main factors:
There are various treatment options available to manage eczema symptoms, one of which is oral steroids. Oral steroids, like topical steroids, can be an effective treatment option in certain circumstances, as they can reduce inflammation and provide significant relief to those who suffer from acute eczema flares. Oral steroids do not eliminate triggers or repair the skin barrier, and therefore are effective only during acute flares for the temporary management of symptoms.
In this blog post, we will delve into the use of oral steroids for eczema, including their mechanism of action, benefits, drawbacks, types, dosages, and administration.
JUMP TO SECTION:
How Do Oral Steroids Work?
Oral steroids, also known as systemic corticosteroids, are used for severe cases of eczema that have not responded to topical treatments. These are medications taken by mouth, usually in the form of tablets or liquid. Unlike topical steroids that work on specific areas where applied, oral steroids work throughout the entire body, providing a more systemic approach to managing severe eczema.
Oral steroids bind to glucocorticoid receptors inside various cells throughout the body. This binding process alters the cell's function and results in several anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects. They inhibit the genes that encode for inflammatory cytokines while promoting the production of anti-inflammatory proteins.
Moreover, oral steroids affect white blood cells (lymphocytes), which play a significant role in the body's immune response. By reducing the number and activity of these cells, oral steroids help limit the immune system's response to inflammation, thus relieving severe and widespread eczema symptoms.(ADC 2000)
The human body as a whole works in concert. Inflammation in one region can affect other areas of the body. Systemic treatments can reach all areas of the body and work to lower inflammation as a whole.
What Are the Benefits of Oral Steroids?
Some people with atopic eczema, may have a mutation where their body’s Th2 immune response is over-triggered, leading to the release of inflammatory cytokines and this begins an excessive or runaway effect in the skin. Due to the mutation, this overactive immune response can be triggered throughout the body.
Excessive inflammation can slow the healing process. Use of systemic steroids during an acute eczema flare to lower inflammation, can allow the skin a break to heal. However, there is limited evidence to support their routine use for eczema.(ROE 2013)
Oral steroids may be considered appropriate for short-term management of severe flares or for allowing patients to participate in important life events.(DRU 2006)
Additionally, oral steroids can be used as a bridging treatment while waiting for slower treatments, such as methotrexate, azathioprine, and mycophenolate, to take effect.(DRU 2006) These slower treatments have safer profiles for long-term use but may take several weeks to start working. Oral steroids can also be considered when other systemic treatments are not suitable or contraindicated.
However, it is important to understand that while oral steroids can help manage symptoms during an acute flare, they are potentially disturbing the natural inflammatory process, and they are not a long-term cure for eczema. Their primary role is to control inflammation and provide symptomatic relief.
For long-term management of eczema, oral steroids should be used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan. A weakened skin barrier, or an excess of triggers in the environment, are critical concerns that need to be addressed in tandem to any symptom relief.
Types of Oral Steroids for Eczema
Oral corticosteroids, or oral steroids, represent a potent treatment option for severe cases of eczema that don't respond to topical treatments. They are powerful anti-inflammatory drugs that work systemically, providing relief from widespread and stubborn eczema symptoms. Here, we will discuss some common oral steroids used for eczema treatment.
- Prednisone: Prednisone, a synthetic derivative of cortisone, is the prodrug of prednisolone, meaning it requires processing in the body before taking effect.(PUC 2022) Hydrocortisone, the typical ingredient in topical steroids, is 4 to 5 times weaker in potency compared to prednisone. Prednisone is often used for short-term treatment during severe eczema flare-ups, typically in a "burst" therapy, where a high dose is prescribed initially, then gradually reduced.
- Prednisolone: Prednisolone, a metabolite of prednisone, has a similar mechanism of action and is equally effective in managing inflammation. It is often used when the patient has liver problems, as prednisolone doesn't need to be converted in the liver like prednisone.
- Methylprednisolone: Methylprednisolone is another type of oral corticosteroid used to treat severe eczema. It also reduces inflammation and suppresses the immune system. Methylprednisolone is often administered in a dose pack, where the dosage is decreased gradually over a period.
- Dexamethasone: Though less commonly used for eczema, dexamethasone is a powerful oral corticosteroid that may be used in some cases. It is typically reserved for extremely severe or refractory cases due to its potency.
It is important to note that while these oral steroids can provide rapid relief from severe eczema symptoms, they are typically not a long-term solution due to potential side effects. The goal of oral steroid treatment is often to quickly control severe symptoms, allowing other long-term management strategies to be implemented effectively.
The specific choice and dose of oral steroids for eczema will depend on several factors, including the severity of symptoms, patient's overall health status, the presence of other medical conditions, and their response to prior treatments. Therefore, the decision should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider, emphasizing the importance of personalized care in eczema management.
Dosage, Use & Administration
When it comes to the administration of oral steroids for eczema, it is vital to follow your healthcare provider's instructions carefully to ensure the medication's effectiveness and safety.
Oral steroids are typically administered in pill or liquid form. The dosage of oral steroids can vary significantly depending on the severity of your eczema, your overall health status, and the specific oral steroid prescribed.
Here are some key considerations regarding the dosage and administration of oral steroids for eczema:
- Short-Term Use: Oral steroids are generally used for short-term "burst" therapy to control the symptoms of severe eczema flare-ups. This typically involves a higher initial dose, which is then tapered down gradually over a period, usually one to two weeks.
- Tapering Off: It's crucial to follow the prescribed schedule and not to stop taking oral steroids abruptly. Since these medications affect your adrenal glands' function, stopping them suddenly could lead to adrenal insufficiency, a serious condition where the body cannot produce enough of certain hormones and induce steroid withdrawal.
- Timing: Oral steroids are usually taken once daily, and it's often recommended to take them in the morning, as this aligns with your body's natural rhythm of steroid production.
- With Food: To help protect your stomach, it's usually suggested to take oral steroids with food or after a meal.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider are crucial when you are taking oral steroids. This monitoring helps assess your response to the treatment and manage any potential side effects promptly.
- Individualized Treatment: Remember, the dosage and administration can vary greatly among individuals. What works well for one person may not work as effectively for another. Hence, your healthcare provider will tailor your treatment plan based on your specific needs.
It is important to stress that oral steroids are powerful medications, and their use must be closely monitored by a healthcare professional. Even though they can provide rapid relief from severe eczema symptoms, their potential side effects necessitate careful administration and adherence to the prescribed dosage.(BAR 2023)
What Are the Drawbacks & Side Effects of Oral Steroids?
The management of atopic dermatitis with systemic corticosteroids, while effective in temporarily suppressing the disease, is generally not recommended due to short and long-term adverse effects and an unfavorable risk-benefit profile.
While oral steroids for eczema can offer rapid and significant relief from severe symptoms, their systemic action means they can also have an impact on other areas of the body, potentially leading to a range of side effects. It is crucial to be aware of these potential side effects, as this understanding can aid in the early detection and management of any adverse effects that may arise during treatment.
Here are some of the common side effects associated with oral steroids:
Weight Gain and Increased Appetite: Oral steroids can stimulate appetite, leading to weight gain in some individuals. Dietary counseling may be beneficial to manage this side effect.
Mood and Sleep Disturbances: Some people may experience mood swings, anxiety, or difficulty sleeping while taking oral steroids.
High Blood Sugar Levels: Oral steroids can raise blood sugar levels, potentially causing or exacerbating diabetes. Individuals with diabetes or at risk of diabetes need close monitoring of their blood sugar levels while taking oral steroids.
Bone Loss (Osteoporosis): Long-term use of oral steroids can lead to osteoporosis, increasing the risk of fractures. Pediatric patients may experience decreased linear growth while on the medication.
High Blood Pressure: Oral steroids can increase blood pressure. Regular monitoring of blood pressure is important for individuals taking these medications.
Eye Conditions: Long-term use of oral steroids can lead to cataracts or glaucoma. Regular eye examinations are recommended for those taking oral steroids for extended periods.
Increased Risk of Infections: Since oral steroids suppress the immune system, they can increase susceptibility to infections. Good hygiene practices and staying up-to-date with vaccinations can help lower this risk.
Adrenal Insufficiency (steroid withdrawal): Use of oral steroids can suppress the body's natural production of steroids. If the medication is stopped abruptly, it can lead to adrenal insufficiency.
These potential side effects underscore the importance of careful monitoring while taking oral steroids for eczema. It is vital to discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider and report any side effects immediately.
Although the list may seem concerning, remember that not everyone experiences these side effects, and for many, the benefits of oral steroids in controlling severe eczema symptoms may outweigh the potential risks. Higher cumulative corticosteroid doses increase the risk of negative outcomes.(BAR 2023)
Oral steroids are not a long-term cure for eczema and flares can return after their use is ended.(SID 2014) Studies have shown that only a small proportion of patients achieve durable remission from only an oral steroid therapy.(SID 2014)
For long-term remission of flares, a weakened skin barrier, or an excess of triggers in the environment, are critical concerns that need to be addressed in tandem to any symptom relief.
Precautions and Contraindications
Given the potential side effects associated with oral steroids, there are several precautions and contraindications to consider before starting this medication for eczema treatment.
Precautions:
- Existing Health Conditions: People with certain health conditions may need to avoid oral steroids or use them with caution. These conditions include diabetes, hypertension, osteoporosis, peptic ulcers, and mental health disorders, among others.
- Infections: Oral steroids can suppress the immune system, making it harder for your body to fight off infections. If you have a bacterial, fungal, or viral infection, your healthcare provider will carefully consider the risks and benefits of using oral steroids.
- Vaccinations: Since oral steroids can suppress the immune response, they may affect the body's response to vaccines. It's crucial to discuss your vaccination status with your healthcare provider before starting oral steroids.
- Other Medications: Oral steroids can interact with a wide range of other medications, altering their effects. Always inform your healthcare provider of all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, you are currently taking.
Contraindications:
While oral steroids can be beneficial for managing severe eczema, they are not suitable for everyone. Contraindications for oral steroids may include:
- Allergy to Steroids: If you've had a previous allergic reaction to oral steroids or any of their ingredients, these medications should be avoided.
- Certain Health Conditions: People with specific health conditions, such as uncontrolled diabetes, active tuberculosis, or certain types of viral infections, may be advised to avoid oral steroids.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Oral steroids may pose risks during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It's essential to discuss these risks with your healthcare provider if you're pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or breastfeeding.
It is important to remember that the decision to use oral steroids for eczema treatment should be made in collaboration with your healthcare provider, considering the severity of your symptoms, your overall health status, and your personal and medical history.
Managing Eczema: Beyond Oral Steroids
While oral steroids can provide rapid relief from severe eczema symptoms, they are not the sole solution for managing this complex skin condition.
Long-term management should include the identification and elimination of triggers and a strengthening of the skin barrier.
Check out our articles on moisturizing, avoiding triggers, and controlling your immune system through diet, and stress management.
Always consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best and most suitable treatment options for your eczema.
Share your experiences with us! Tell us what has and hasn’t worked for you. What did we miss in this article that you've found personally impactful? Your insights can help others better understand and manage their eczema.