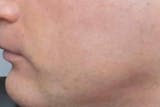
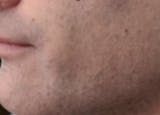
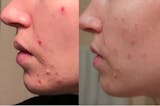
Primary care, dermatologists, allergists, dieticians, psychologists, and eczema specialists can help with various aspects of eczema support.
We help you understand when to connect with these providers and how to communicate your needs clearly.
Introduction
Eczema, affecting millions of individuals globally, is a recurring skin condition typified by red, itchy, and inflamed skin outbreaks. The degree and length of these flare-ups are influenced by three key factors:
Most eczema flares, and the overarching long-term condition, can be managed by the individual finding and eliminating triggers, strengthening or supplementing their skin barrier, and using other over-the-counter medication.(SID 2014)
However, for many managing this condition requires the help and support of a healthcare professional.
In this article, we will delve into the role of various healthcare professionals and when it might be time to see a doctor to provide you with a comprehensive understanding that will empower you to take control of your eczema.
JUMP TO SECTION:
Deciding When to Consult a Doctor For Eczema
Visiting a doctor can indeed require a significant investment of time and resources. During your initial consultation, physicians often wish to understand the steps you have already taken to manage your eczema symptoms, and they may recommend that you continue or augment these strategies before escalating to more advanced treatments.
However, it is crucial not to delay seeking medical assistance if you feel it's necessary.
To support you during these early discussions with your healthcare provider, we've compiled the following recommendations.
First-Line Approaches: Self-Directed Treatments
Self-care strategies and lifestyle changes can be effective in managing mild to moderate eczema symptoms. Here are some key practices you can implement at home:
Proper Skin Care
Adopting a diligent skin care routine is fundamental in managing eczema. Regularly moisturizing your skin can bolster your skin's natural barrier, mitigate dryness and itching, and prevent flare-ups.
Opt for a fragrance-free, hypoallergenic moisturizer, applying it shortly after bathing to lock in moisture. Additionally, avoid harsh soaps and detergents and bathe in lukewarm rather than hot water to minimize skin irritation.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Certain modifications to your daily routine can positively influence your eczema management. Techniques for stress reduction, such as yoga or meditation, may be beneficial, as stress can trigger eczema flare-ups for some individuals.
Regular physical activity, a nutritious diet, and sufficient sleep can also contribute to overall wellbeing and potentially alleviate eczema symptoms.
Trigger Management
If you are aware of specific triggers for your eczema—certain foods, materials, or allergens, for instance—avoiding these can help to stave off flare-ups. Over time, you may be able to discern patterns and manage your condition more effectively.
Knowing When to Seek Medical Attention for Eczema
Recognizing when professional intervention is necessary is critical for effective eczema management. Here are several signs that you should consult a healthcare professional:
Persistent Symptoms: If your eczema symptoms persist or worsen despite your best efforts at self-care and over-the-counter treatments, it is time to consult a doctor. Persistent itching, redness, and dryness need professional attention to prevent further complications such as skin infections and scarring.
Severe Flare-ups: Experiencing severe eczema flare-ups characterized by intense itching, extensive rash coverage, or discomfort that interrupts sleep and daily activities, is a signal that it is essential to seek medical help promptly.
Signs of Infection: Eczema can compromise the skin's barrier function, making it more susceptible to infections. If you notice increased redness, swelling, warmth, pain, or pus in or around the areas of eczema, or if you develop a fever, these could be signs of a skin infection requiring immediate medical attention.
Impact on Quality of Life: If eczema is causing significant distress, impacting your sleep, or affecting your mental health, these are compelling reasons to seek professional help. Remember, your emotional well-being is just as important as your physical health.
Ineffectiveness of Current Treatment: If your current prescription treatment is not providing the relief it once did, or if you are experiencing troubling side effects, a healthcare professional can reassess your condition and potentially adjust your treatment plan.
The Role of Medical Professionals In Eczema Treatment
The quality, availability and affordability of healthcare varies around the world and each place will have its own challenges. Free services can have low capacities resulting in limited and brief appointments with long wait-times. There may be limited budgets and therefore expensive treatments may only be offered in the most severe cases.
On the other hand, paid service can be cripplingly expensive and when healthcare operates like a business, there is a conflict of interest between appropriate and profitable prescriptions. Subsequently, it is crucial to know what you can gain from a doctor’s appointment and how to work with them to get what you need.
Various healthcare professionals each play a vital role in diagnosing, treating, and managing eczema, each focusing on different aspects of the condition.
It is helpful to bear in mind that eczema is a coming together of:
Trigger intensity
Skin barrier strength
Immune system activity
While all of these practitioners will have training in all three areas, they do tend to specialize. We present the areas they specialize in below to help guide you to the right practitioner who can help with your eczema.
Primary Care Providers
Specializing in the following areas related to eczema:
Trigger intensity
Skin barrier strength
Immune system activity
The frontline clinicians in healthcare, primary care providers are often the first professionals you will consult about your eczema symptoms. They can provide the initial prescriptions for eczema, such as topical corticosteroids, and are typically well-versed in identifying potential triggers of eczema flare-ups. They may also screen you for conditions associated with eczema or that lower your threshold to triggers.
With a more holistic view of your health, primary care providers can also make critical referrals to allergists, dermatologists, and eczema specialists, if your condition necessitates more specialized care. A primary care provider are experts in coordinating care and fascilitating all of the pieces that need to come together in a successful treatment plan.
They are also fantastic for providing feedback on your self-directed care and providing advice on washing, moisturizing, and antihistamines.
Dermatologists
Specializing in the following areas related to eczema:
Assessing Skin Barrier Strength
Evaluating Skin-Specific Immune System Activity
Dermatologists excel at deciphering complex skin conditions, particularly when multiple diseases or infections are present concurrently. A dermatologist is often consulted when flare symptoms are severe, persist despite initial treatment, or when skin infections or chronic medical issues complicate the condition.
Dermatologists are skilled in prescribing a broad spectrum of topical and systemic medications aimed at controlling inflammation including:
Topical calcineurin (TC) inhibitors: These medications help reduce inflammation and are an alternative to topical steroids.
Phototherapy: Controlled exposure to ultraviolet light can help improve eczema symptoms by reducing inflammation and itchiness.
Monoclonal Antibodies: subcutaneous injections which block proteins contributing to inflammation, used in moderate to severe eczema cases.
Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors: These oral or topical medications work to reduce inflammation by targeting specific immune pathways.
Immunosuppressants: Medications like cyclosporine and methotrexate suppress the immune system to control severe eczema symptoms.
Oral Steroids: Reserved for severe cases, these medications offer short-term relief by suppressing inflammation throughout the body.
Allergists
Specializing in the following areas related to eczema:
Identifying Triggers
Evaluating immune system activity
While measures to suppress the immune system can provide temporary relief during a flare, long-term control of eczema often requires identifying and managing triggers. Allergists are experts in pinpointing these triggers, particularly those related to allergies and intolerances.
Allergists employ various allergy tests to identify these triggers, providing a comprehensive picture of what may contribute to your eczema flare-ups. Once these triggers are identified, allergists offer strategies to either avoid or manage them effectively, thus helping reduce the occurrence and severity of eczema flare-ups.
In the course of managing your eczema, allergists may recognize the need for dietary interventions to manage food-related triggers. In such instances, they can make referrals to dietitians.
Registered Dietitian or Nutritionist
Specializing in the following areas related to eczema:
Identifying Trigger Intensity in the Gut
Evaluating Immune System Activity in the Body
Dieticians and nutritionists play a crucial role in helping you identify potential dietary triggers for eczema. Hidden ingredients in your food could be causing or exacerbating your symptoms, and a dietician can help you safely navigate and adjust your diet.
Furthermore, dietitians and nutritionists can provide guidance on adopting an anti-inflammatory or eczema-friendly diet, which may help manage your symptoms. By ensuring that your body is receiving the necessary nutrients, a dietician not only supports the overall health of your body but can also contribute to the management and prevention of eczema flare-ups.
Eczema Specialists
Specializing in the following areas related to eczema:
Trigger intensity
Skin barrier strength
Immune system activity
While some medical team members may not be delving as deeply into your specific case, this is where eczema specialists can shine!
Eczema specialists provide an integrated approach to managing eczema, combining elements of dermatology and allergy expertise with a focus on long-term management strategies.
They often delve deeper into lifestyle and self-directed solutions and work to develop a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your specific needs and circumstances.
Psychologists and Mental Health Practitioners
While psychologists and mental health practitioners may not directly specialize in the treatment of eczema, they can have a powerful impact on the disease. They provide support in managing stress and enhancing mental health, both of which can significantly impact the activity of the immune system.
Stress and poor mental health can exacerbate eczema symptoms and trigger flare-ups. Working with a psychologist or mental health practitioner (such as a mental health coach) can provide coping strategies and therapeutic interventions that help reduce stress levels and promote mental wellbeing
How to Work With a Doctor
Maintaining open and effective communication with your doctor is fundamental to managing eczema successfully. Fostering a collaborative relationship with your healthcare professional allows for a deeper understanding of your condition and ensures a more personalized treatment approach.
It is important to remember that conventional Western medicine often focuses on treating each condition as an isolated problem, with specific medications prescribed to address specific conditions and symptoms. Therefore, doctors trained in this model will tend to focus on observable or measurable symptoms.
Unfortunately, eczema is often a disease of multiple factors.
Tracking your symptoms and experiences can help immensely in communicating the complexity of your condition and showing the observable and measurable symptoms over time. Regularly documenting your eczema flare-ups, triggers, and response to treatment can provide your doctor with valuable insights and help tailor your treatment plan. Try to share this information prior to your visit so the doctor has additional time to review.
If you are concerned about topical steroids and your doctors approach after discussing with them, we highly recommend tracking and sharing your tracking data with your team and ask to discuss additional treatment options after they review it. This may require a follow up visit if you have not provided your symptom tracking information prior to the initial visit.
Managing Symptoms Without Medical Intervention
Alongside medical treatments, self-directed treatments and lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in managing mild to moderate eczema symptoms. Here are some strategies that you can employ at home:
Skin Barrier Care: Good skin care is the cornerstone of managing eczema. Keeping your skin “moisturized” has long been the motto and moisturizers can help temporarily relieve symptoms. Newer moisturizers include components like ceramides and prebiotics for the microbiome to go farther and actively support skin barrier strength and repair.
Systemic Immune Modulation: Certain lifestyle changes can positively impact your immune regulation. Regular exercise, a low inflammation diet, and adequate sleep can also contribute to overall immune control and potentially improve eczema symptoms.
Trigger Management: Finding and avoiding triggers can help to prevent flare-ups. Over time, you may be able to identify patterns and better manage your condition.
What Next?
Eczema is more than just a skin condition—it's a multifaceted interaction between your immune system, external triggers, and your skin's natural defenses. Managing it effectively often requires a combination of professional medical treatment, self-care practices, and lifestyle adjustments.
Healthcare professionals, including primary care providers, dermatologists, allergists, and eczema specialists, all play vital roles in diagnosing, treating, and managing eczema. They can provide a range of prescription treatments and guide you in making lifestyle changes to manage your symptoms effectively.
Share your experiences with us!
Tell us what has and hasn’t worked for you. What did we miss in this article that you've found personally impactful? Your insights can help others better understand and manage their eczema.